
|
|
Related:
|
|
|
|
|
Basal Cell Cancer Treatment
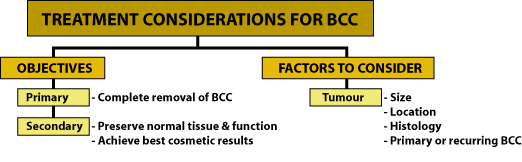
Most basal cell carcinomas may be treated by one of the following methods. The choice of treatment is influenced by:
- size, location, type, and grade of tumour
- person's age and health
- whether the tumour is primary or has come back after treatment (recurred)
- availability of the treatment
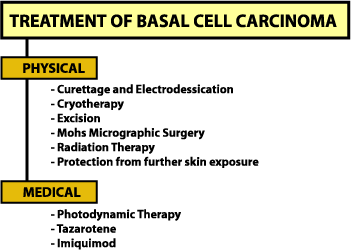
The following represent the range of treatments of available for basal cell carcinoma:
Imiquimod (Aldara)
- Aldara has recently been approved for the treatment of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
More information about Aldara, including how it works and clinical results.
Curettage and Electrodesiccation (C & E)
- used for small lesions that are less than 2 cm
- not used for lesions on areas where the cancer is likely to recur (nose, lips, eyelids, ears, scalp, temple)
Surgery (Wide Excision)
- the tumour is removed along with a margin of cancer-free skin
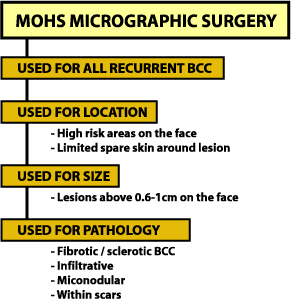
Mohs Micrographic Surgery
- used for all types of basal cell cancers
- commonly used for:
- areas that are at high risk of recurrence (eyelids, nose, ears, forehead, scalp), as well as lesions that have already recurred
- lesions that are larger than 2 cm, as well as lesions with poorly defined borders
- areas where maintaining function and appearance are important
- invasive lesions that have spread to underlying cartilage or bone
- tumours that have been left untreated for a long time
- people with nevus basal cell carcinoma syndrome
- it involves a meticulous study of tissues removed by a pathologist at the time of surgery
Radiation Therapy
- used for:
- small to medium sized primary basal cell carcinoma lesions
- ensuring cancer free margins after surgery
- lesions that have recurred after surgery
- relief or to control symptoms of very large tumours
- people who are unable or unwilling to undergo surgery
- not used for:
- people with nevus basal cell carcinoma syndrome
- sclerosing or morpheaform Basal Cell Carcinoma
Chemotherapy
- topical chemotherapy (5-Fluorouracil (5-FU)) may be used for:
- superficial tumours
- people who are unwilling or unable to undergo surgery or radiation
- people with nevus basal cell carcinoma syndrome
- the elderly who can’t tolerate other treatments
- systemic chemotherapy may be used for basal cell carcinoma that has spread to other parts of the body
Immune Response Modifiers
- Imiquimod 5% Cream (Aldara™) has recently been approved in Canada and the US to treat Superficial Basal Cell Cancer (sBCC)
- Imiquimod’s novel mechanism of action stimulates the body’s own natural defenses to target diseased tissue
- It stimulates the innate immune response through interferon-a production, as well as acquired immunity by activating T-helper 1 cells
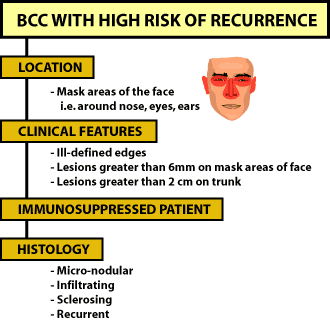
Recurrence of Cancer
|