Actinic Keratosis - A Definition
Actinic Keratoses are formed in the epidermis. They are also known as Solar Keratoses. They are identified by atypical changes in the keratinocytes which are the cells making up most of the epidermis. There is a debate as to whether they are precancerous or whether they are all skin cancers from the start, being part of a continuum from early signs to fully formed cancer called Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
Some actinic keratoses become invasive squamous skin cancer. The presence of actinic keratosis is a marker for other skin cancers such as basal cell carcinomas. They affect older men preferentially and the prevalence may be as high as 40% in fair-skinned people over the age of 50. They account for at least 14% of visits to dermatologists and in warmer climates probably much more.
Images
Click on any of the Actinic Keratosis images below to enlarge.
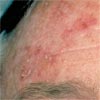
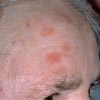
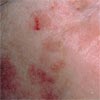
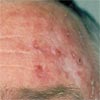
What else looks like Actinic Keratosis
Hypertrophic Actinic keratosis- this is a thickened red scaly lesion
consider
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Warts
- Irritated seborrhoeic keratosis
- Basal cell carcinoma-multifocal type especially when on the trunk
Pigmented actinic keratosis
consider
- Lentigo maligna
- Melanoma in situ ( in situ = within the epidermis)
- Pigmented basal cell cancer
Where it is found
It is always seen on the sun-exposed areas of the face, backs of the hands, forearms as well as on the legs. It is seen also on the scalp of bald men as well as on the ears and lips. When the lips are involved, the condition is termed actinic cheilitis. It becomes more common with age.
When does it occur
It may be first seen in the 30ís. It is estimated that 80% of those with fair skin over 70 years will have actinic keratoses.
Symptoms
Early actinic keratosis can often be detected by feeling the skin. There are small areas of discrete roughness to the skin. At this stage the lesions are skin coloured or slightly brown. They may become pink or reddish as they enlarge. Most of the lesions are usually 1-3 mm although they may be as large as 1-2 cm in diameter. Some become much thicker than others, tending to grow outwards from the skin and are known as hypertrophic actinic keratosis or a cutaneous horn. When an actinic keratosis starts to thicken the question always to ask is if there are changes developing that indicate a true invasive Squamous cell cancer. Usually, but not always, there is thickening within the body of the skin in true squamous cell cancers which is called induration.
Actinic chelitis is seen usually on the lower lip. The lip lines are often indistinct and there are white changes called leukoplakia. Scaling and redness is sometimes seen and the skin may develop some small erosions and crusting.
Back to Actinic Keratosis Basics |
Top
|